Association Analysis
As life studies enter the post genomic era, systems biology approaches are gradually becoming mainstream. As an important research strategy in systems biology, multi omics joint analysis has become a research hotspot in recent years. Multi omics studies have several advantages over single omics:
- Ability to systematically delineate regulatory processes, increasing data integrity;
- Mutual validation is possible between multi omics data, strengthening the credibility of conclusions;
- The joint analysis of multi omics data is more conducive to the study of regulatory mechanisms of biological processes and improves the innovation of research.
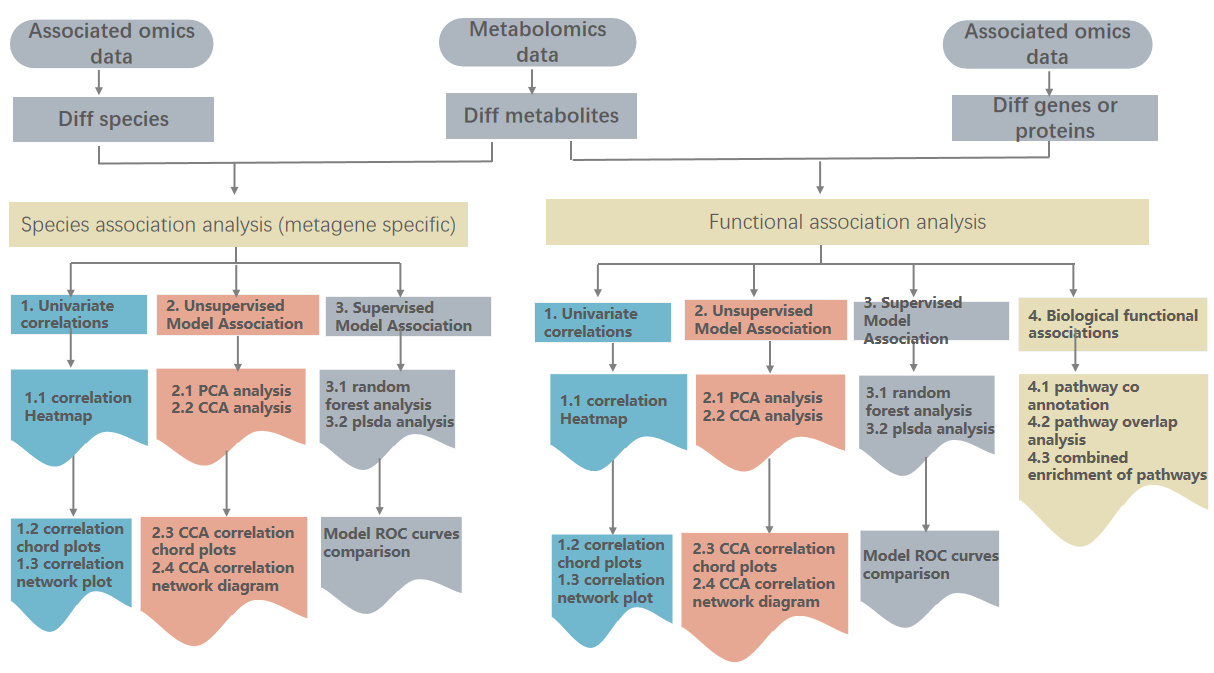
Current thinking about integrative analysis of metagenomics and metabolomics can be mainly divided into the following categories:
- To analyze the correlation between species and metabolites and the correlation between functional genes and metabolites, respectively, by univariate pairwise correlation or by multivariate model correlation analysis, to define the expression correlation law and to reveal the expression regulation law from multiple dimensions by clustering heatmaps, correlation network plots as well as chordomograms;
- Search for combined biomarkers of species and metabolic and functional genes and metabolism separately: to define the combined marker combinations that contributed most to the grouping by multi omics models and to analyze the predictive effect of the combined marker combinations on the phenotype;
- Integrating metagenomic, metabolomic data based on biological pathways: finding differentially functional genes and differential metabolites involved in a certain important metabolic pathway or analyzing the pathways to which functional genes and metabolism are jointly enriched to define the key pathways related to biological phenotypes. Association analysis for metabolomics and metagenomics is to utilize differential metabolites with quantitative values of differential species and differential functional genes, respectively, for joint analysis.
In this report, association analysis will be conducted from both the metabolite + species level and the metabolite + functional gene level. In the association analysis, univariate correlation, unsupervised Model Association, supervised Model Association, and biological function association were comprehensively used.
The specific association analysis flowchart is shown below: